Case History
Patient: Female, 66 years old
Complaint:
- Blurred near vision
- Adequate distance vision, but details are not clear
- Never wore distance glasses, only reading glasses
Past medical history:
- No eye problems
- No previous eye appointments
- Good general health
- Allergic to seafood
Visual habits:
- Uses her eyes for general activities, such as cooking, watching TV, using her phone, and reading
Preliminary eye exam:
- Visual acuity (VA) with correction (VAsc): OD 20/40, OS 20/30
Refraction:
- Retinoscopy:
- OD +3.75-0.75x45 VA 20/20
- OD +3.00-0.25x60 VA 20/25
- Monocular subjective:
- OD +3.75-0.75x45 VA 20/20
- OD +2.75-0.25x60 VA 20/20
- Best corrected visual acuity (BVA):
- OD +3.75-0.62x70 VA 20/20
- OD +2.75-0.25x47 VA 20/20
- OU 20/15
Binocular function at distance (6 m):
- Horizontal phoria: Ortho
- Vertical phoria: Ortho
Functional near vision (40 cm):
- Base curve convergence (BCC): +2.00D
- Near refraction astigmatism (NRA) / near refraction astigmatism (PRA): +0.75/-0.75 (rely BCC)
Assessment:
- Compound hyperopic astigmatism
- Normal binocular function
- Presbyopic
Plan:
- Full prescription:
- OD +3.75-0.62x70
- OD +2.75-0.25x47
- Progressive addition lens (PAL) prescription: Add +2.00
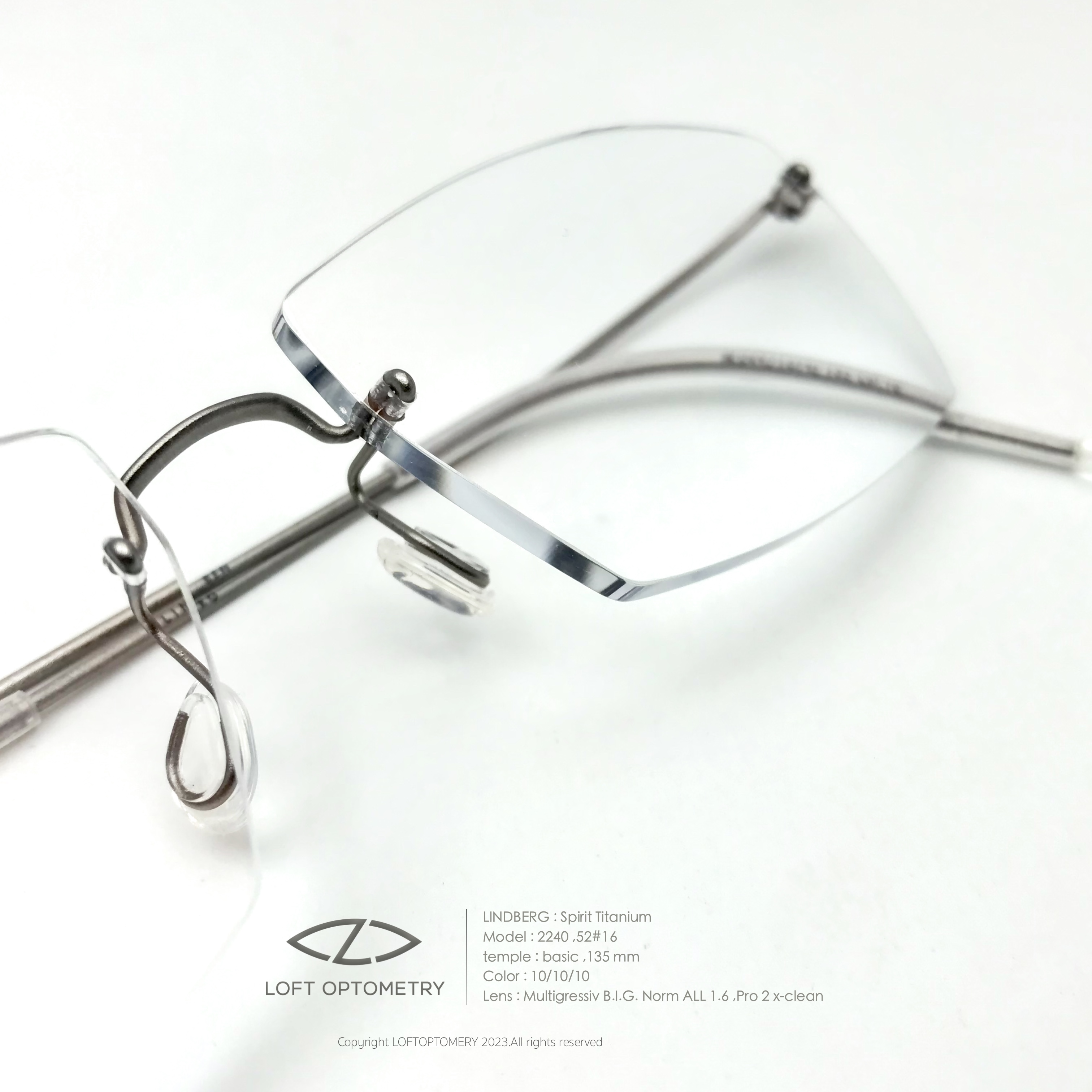
- Lens : Rodenstock Multigressiv B.I.G. Norm 1.6 w/ Solitare protect pro2 +extra clean
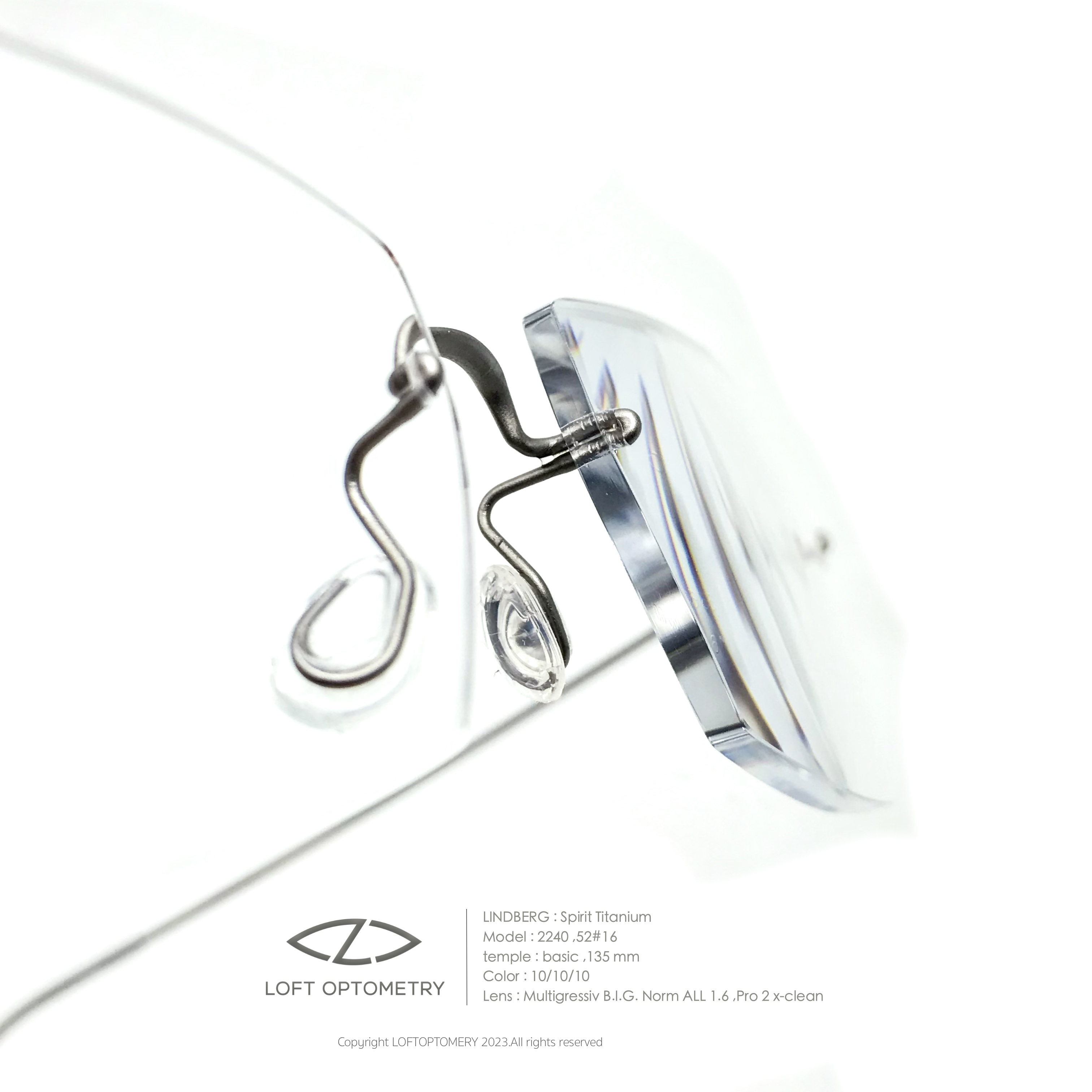
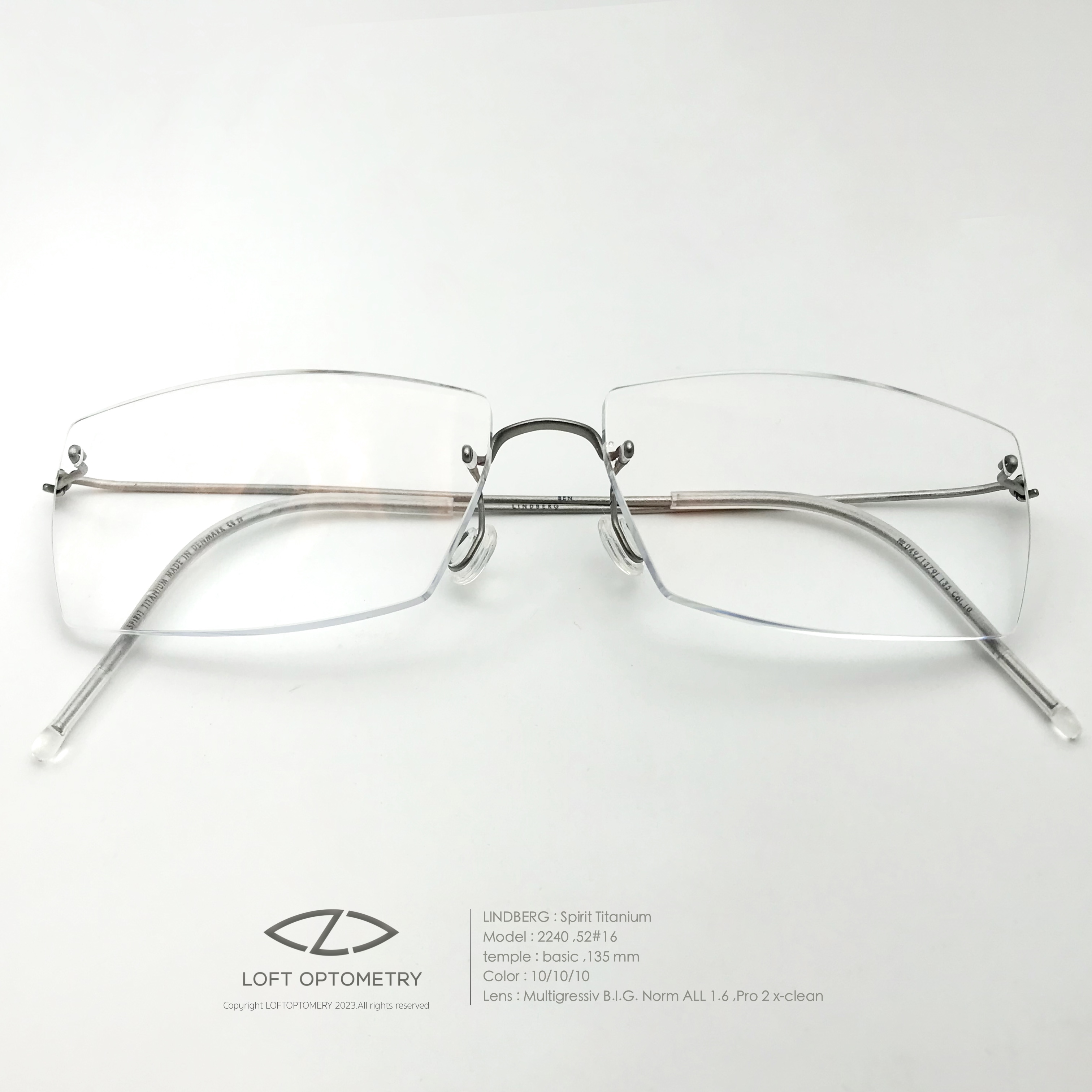
- Frame : Lindberg spirit custom spec
Interpretation
This patient is a 66-year-old woman with blurred near vision and adequate distance vision. She has a history of reading glasses, but she has never worn distance glasses.
Her preliminary eye exam shows that her vision is improved with correction. She has compound hyperopic astigmatism, which means that she has both hyperopia (farsightedness) and astigmatism (a refractive error that causes images to be blurry or distorted). She also has presbyopia, which is a normal age-related condition that causes difficulty with near vision.
Her binocular function is normal, which means that her eyes work together properly.
Based on her assessment, the doctor recommends a full prescription for distance and near vision. The full prescription is +3.75-0.62x70 for the right eye and +2.75-0.25x47 for the left eye. The PAL prescription is +2.00 add, which means that the patient will need to wear reading glasses with a +2.00 power to improve her near vision.
Discussion
This case presents with hyperopia and astigmatism in the distance, and presbyopia in the near. The correction is straightforward, as the doctor simply prescribes the full amount of correction for each eye.
However, there are some concerns for patients with high hyperopia, such as the center thickness of the lens. Because the eye is hyperopic, the lens will be thicker in the center. Using a larger lens will make the center of the lens even thicker. Additionally, certain types of thin frames, such as rimless frames, require a thick edge to allow for the insertion of the wire or metal. This can make it difficult to achieve a thin lens.
In this case, I chose a drilled frame that was not too large. This was done because I could calculate where the thinnest point of the lens would be. If the thinnest point was not at the drilled location, then the drilled frame would not be a problem. However, this is a case-by-case decision, and it may not be suitable for all patients.
The results of the progressive lens treatment in this case were successful sooner than expected. The patient had never worn progressive lenses before, but she was able to adapt to them immediately on the first try. This is impressive considering that the patient had such high hyperopia.
In conclusion, even patients with high hyperopia and no previous experience with glasses can be successfully treated with progressive lenses. Modern lenses are very advanced, and they do not require the doctor to under-correct the distance vision and then over-correct the near vision. This would reduce the visual field of the progressive lens, making it more difficult to see and adapt to.
In addition, the addition power should be based on the BCC(binocular cross cylinder) measurement, not on the patient's age. In this case, the patient was 66 years old, but her BCC measurement indicated that she only needed an addition power of +2.00D. If the doctor had under-corrected the distance vision, the patient would have needed to increase the addition power later, which would have been more difficult.
That's all for this brief case report.
Dr.loft,O.D.
Loft Optometry
578 Wacharapol rd, Tha-rang ,Bangkhen ,BKK 10220
Mobile :090-553-6554
LineID : loftoptometry
www.faecbook.com/loftoptometry
Product
Frame : Lindberg Spirit
Temple : Basic , color 10 : raw-titanium , length 135 mm
Bridge : M ,flat ,clip-length 3.5 mm
Temple clip : col.10 / length 3.5 mm
Lens : Rodenstock Multigressive B.I.G. Norm 1.6 w/ Solitaire Protect Pro-2 x-clean

ขอบคุณทุกท่านสำหรับการติดตาม
ดร.ลอฟท์ ,O.D.

ทำนัดเพื่อเข้ารับบริการ
578 ถ.วัชรพล ท่าแร้ง บางเขน กทม 10220
Mobile : 090-553-6554
Line id : loftoptometry
maps : LOFT OPTOMETRY MAPs
Product
Frame : Lindberg Spirit
Temple : Basic , color 10 : raw-titanium , length 135 mm
Bridge : M ,flat ,clip-length 3.5 mm
Temple clip : col.10 / length 3.5 mm
Lens : Rodenstock Multigressive B.I.G. Norm 1.6 w/ Solitaire Protect Pro-2 x-clean